On homomorphisms between locally convex spaces
Abstract
Homomorphisms 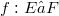 between locally convex spaces
between locally convex spaces 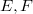 , i.e. continuous linear maps which are open onto the range, occur quite often and they are nice to handle.Unfortunately, the stability properties of the class of homomorphisms are poor.For instance, a homomorphism
, i.e. continuous linear maps which are open onto the range, occur quite often and they are nice to handle.Unfortunately, the stability properties of the class of homomorphisms are poor.For instance, a homomorphism 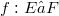 will in general not remain a homomorphism, if E and F are endowed with, for instance, their strong topology; the transpose
will in general not remain a homomorphism, if E and F are endowed with, for instance, their strong topology; the transpose 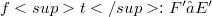 will usually not be a homomorphism, and the behaviour of the bitranspose is still worse. The investigation of homomorphisms has a good tradition,in fact, it goes back to Banach and was dealt with afterwards by Dieudonné, L. Schwartz, Grothendieck and Köthe (see for example [12]). The purpose of this article is twofold: first, to study the stability behaviour of the class of homomorphisms with a bit of a systematic touch (see (1.4),(1.8), (2.3), (2.5)); and second, to apply new methods and results from the recent development of the structure theory of Fréchet,
will usually not be a homomorphism, and the behaviour of the bitranspose is still worse. The investigation of homomorphisms has a good tradition,in fact, it goes back to Banach and was dealt with afterwards by Dieudonné, L. Schwartz, Grothendieck and Köthe (see for example [12]). The purpose of this article is twofold: first, to study the stability behaviour of the class of homomorphisms with a bit of a systematic touch (see (1.4),(1.8), (2.3), (2.5)); and second, to apply new methods and results from the recent development of the structure theory of Fréchet, 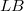 - and
- and 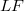 -spaces to the context of homomorphisms. For instance, we obtain a(nother) characterization for the quasinormability of Fréchet spaces E by the property that for every monomorphism
-spaces to the context of homomorphisms. For instance, we obtain a(nother) characterization for the quasinormability of Fréchet spaces E by the property that for every monomorphism 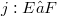 with F Fréchet, j remains a homomorphism for the topology of uniform convergence on strongly compact sets both on E and on F (see (1.9), (1.10)).Proposition (2.7) presents a general background for the fact that for the famous quotient map
with F Fréchet, j remains a homomorphism for the topology of uniform convergence on strongly compact sets both on E and on F (see (1.9), (1.10)).Proposition (2.7) presents a general background for the fact that for the famous quotient map 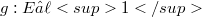 with E Fréchet Montel, the transpose is not a monomorphism for the weak (sic!) topologies. In section 3, where we deal with the bitranspose of homomorphisms, we give an example of a quotient map
with E Fréchet Montel, the transpose is not a monomorphism for the weak (sic!) topologies. In section 3, where we deal with the bitranspose of homomorphisms, we give an example of a quotient map 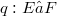 with E Fréchet such that
with E Fréchet such that 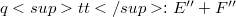 is not a homomorphism between the strong biduals. Finally, we present a fairly general condition on a strict
is not a homomorphism between the strong biduals. Finally, we present a fairly general condition on a strict 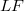 -space, under which its strong bidual will again be an
-space, under which its strong bidual will again be an 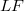 -space.
-space.
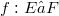 between locally convex spaces
between locally convex spaces 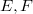 , i.e. continuous linear maps which are open onto the range, occur quite often and they are nice to handle.Unfortunately, the stability properties of the class of homomorphisms are poor.For instance, a homomorphism
, i.e. continuous linear maps which are open onto the range, occur quite often and they are nice to handle.Unfortunately, the stability properties of the class of homomorphisms are poor.For instance, a homomorphism 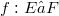 will in general not remain a homomorphism, if E and F are endowed with, for instance, their strong topology; the transpose
will in general not remain a homomorphism, if E and F are endowed with, for instance, their strong topology; the transpose 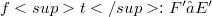 will usually not be a homomorphism, and the behaviour of the bitranspose is still worse. The investigation of homomorphisms has a good tradition,in fact, it goes back to Banach and was dealt with afterwards by Dieudonné, L. Schwartz, Grothendieck and Köthe (see for example [12]). The purpose of this article is twofold: first, to study the stability behaviour of the class of homomorphisms with a bit of a systematic touch (see (1.4),(1.8), (2.3), (2.5)); and second, to apply new methods and results from the recent development of the structure theory of Fréchet,
will usually not be a homomorphism, and the behaviour of the bitranspose is still worse. The investigation of homomorphisms has a good tradition,in fact, it goes back to Banach and was dealt with afterwards by Dieudonné, L. Schwartz, Grothendieck and Köthe (see for example [12]). The purpose of this article is twofold: first, to study the stability behaviour of the class of homomorphisms with a bit of a systematic touch (see (1.4),(1.8), (2.3), (2.5)); and second, to apply new methods and results from the recent development of the structure theory of Fréchet, 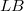 - and
- and 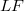 -spaces to the context of homomorphisms. For instance, we obtain a(nother) characterization for the quasinormability of Fréchet spaces E by the property that for every monomorphism
-spaces to the context of homomorphisms. For instance, we obtain a(nother) characterization for the quasinormability of Fréchet spaces E by the property that for every monomorphism 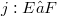 with F Fréchet, j remains a homomorphism for the topology of uniform convergence on strongly compact sets both on E and on F (see (1.9), (1.10)).Proposition (2.7) presents a general background for the fact that for the famous quotient map
with F Fréchet, j remains a homomorphism for the topology of uniform convergence on strongly compact sets both on E and on F (see (1.9), (1.10)).Proposition (2.7) presents a general background for the fact that for the famous quotient map 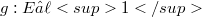 with E Fréchet Montel, the transpose is not a monomorphism for the weak (sic!) topologies. In section 3, where we deal with the bitranspose of homomorphisms, we give an example of a quotient map
with E Fréchet Montel, the transpose is not a monomorphism for the weak (sic!) topologies. In section 3, where we deal with the bitranspose of homomorphisms, we give an example of a quotient map 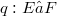 with E Fréchet such that
with E Fréchet such that 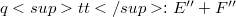 is not a homomorphism between the strong biduals. Finally, we present a fairly general condition on a strict
is not a homomorphism between the strong biduals. Finally, we present a fairly general condition on a strict 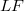 -space, under which its strong bidual will again be an
-space, under which its strong bidual will again be an 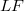 -space.
-space.DOI Code:
10.1285/i15900932v12p27
Full Text: PDF


